Binary search trees are data structure that can be used to store data more efficiently - such that it can be searched and retrieved. [1]
Actions
Table of contents
Open Table of contents
Definition
Binary search trees are another data structure that can be used to store data more efficiently such that it can be searched and retrieved. You can imagine a sorted sequence of numbers.
Visualization
You can imagine a sorted sequence of numbers.
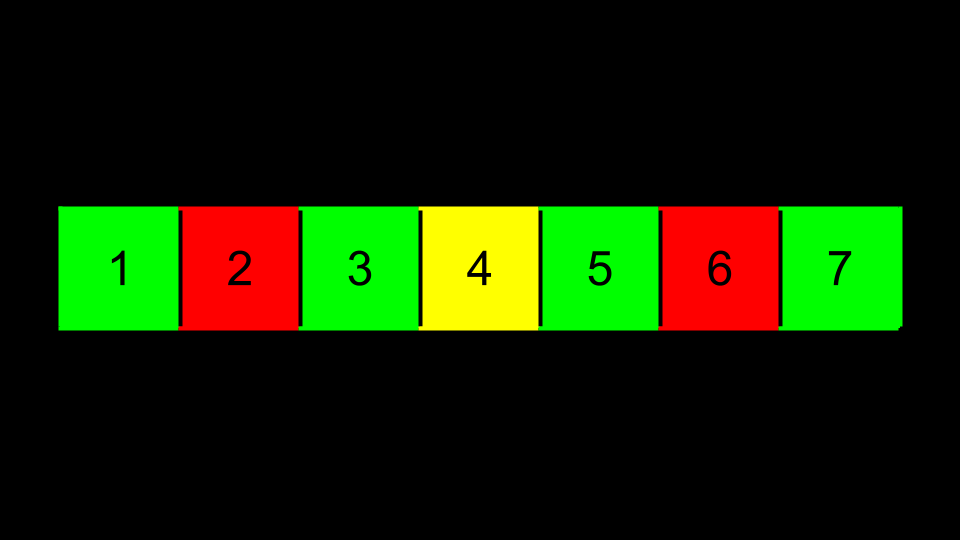
Imagine then that the center value becomes the top of a tree. Those that are less than this value are placed to the left. Those values that are more than this value are to the right.
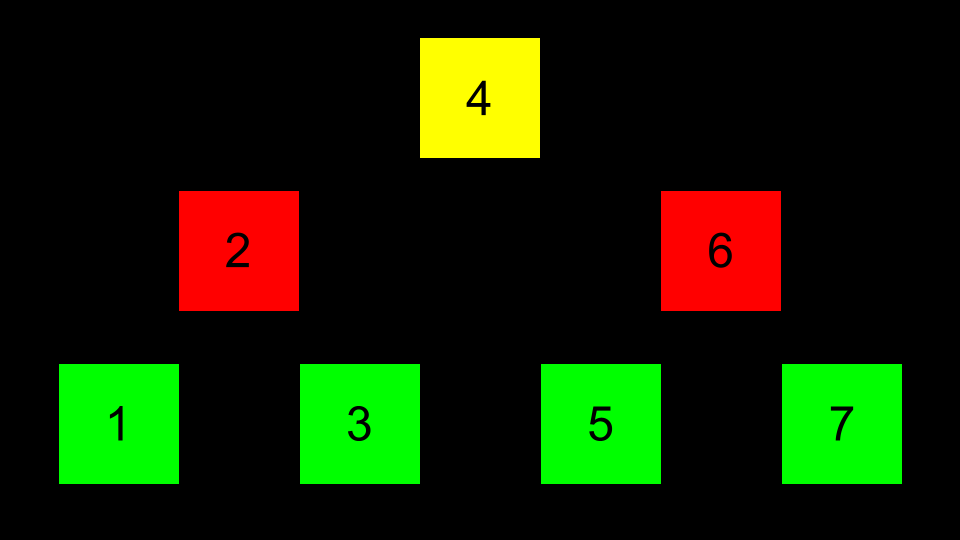
Pointers can then be used to point to the correct location of each area of memory such that each of these nodes can be connected.
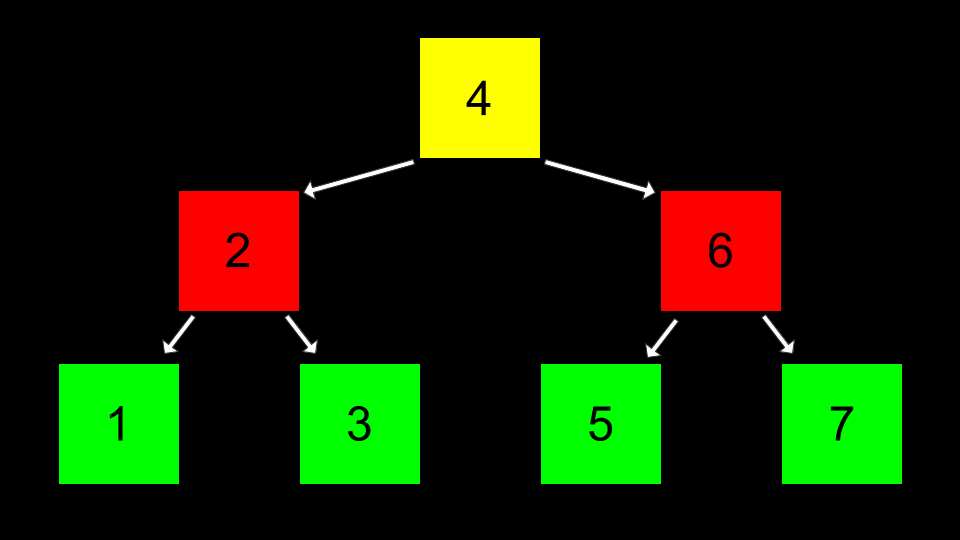
Code
In code, this can be implemented as follows.
// Implements a list of numbers as a binary search tree
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Represents a node
typedef struct node
{
int number;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
}
node;
void free_tree(node *root);
void print_tree(node *root);
int main(void)
{
// Tree of size 0
node *tree = NULL;
// Add number to list
node *n = malloc(sizeof(node));
if (n == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
n->number = 2;
n->left = NULL;
n->right = NULL;
tree = n;
// Add number to list
n = malloc(sizeof(node));
if (n == NULL)
{
free_tree(tree);
return 1;
}
n->number = 1;
n->left = NULL;
n->right = NULL;
tree->left = n;
// Add number to list
n = malloc(sizeof(node));
if (n == NULL)
{
free_tree(tree);
return 1;
}
n->number = 3;
n->left = NULL;
n->right = NULL;
tree->right = n;
// Print tree
print_tree(tree);
// Free tree
free_tree(tree);
return 0;
}
void free_tree(node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
free_tree(root->left);
free_tree(root->right);
free(root);
}
void print_tree(node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
print_tree(root->left);
printf("%i\n", root->number);
print_tree(root->right);
}
Key Takeaways
-
Notice this search function begins by going to the location of
tree. Then, it uses recursion to search fornumber. Thefree_treefunction recursively frees the tree.print_treerecursively prints the tree. -
A tree like the above offers dynamism that an array does not offer. It can grow and shrink as we wish.
-
Further, this structure offers a search time of
O(log n)
Simulation
Below is the BST Animation by Y. Daniel Liang. Can refer other simulation, e.g. [2] and [3].
References
- CS50’s Introduction to CS50’s Introduction to Computer Science. cs50.harvard.edu/x/2024. (Week 5: Data Structures, Section: Notes, Video)